Introduction: What is a Sterile Processing Tech?
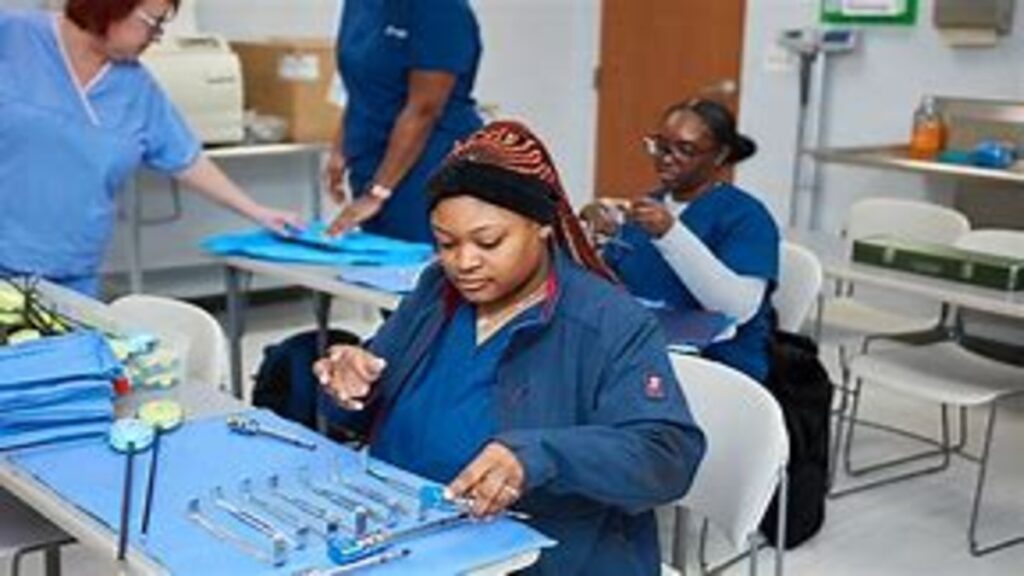
Sterile Processing Tech. Every successful surgery or medical procedure relies on tools that are 100% sterile and safe to use. But have you ever wondered who ensures that these instruments are properly cleaned, disinfected, and ready to go? That’s where Sterile Processing Technicians (also known as Central Service Technicians or SPD Tech) come in.
These professionals may work behind the scenes, but their role is crucial in maintaining the safety and effectiveness of healthcare facilities. In this article, we’ll dive deep into what sterile processing techs do, how to become one, and why they’re so vital to modern medicine.
What Does a Sterile Processing Technician Do?
A Sterile Processing Technician is responsible for cleaning, sterilizing, assembling, and organizing medical instruments and equipment used in surgeries and procedures. They work mainly in hospitals, surgical centers, and other healthcare facilities.
Key Duties Include:
- Cleaning and decontaminating surgical instruments
- Operating sterilization equipment (like autoclaves)
- Assembling and packaging surgical trays
- Inspecting tools for damage or malfunction
- Maintaining inventory of medical supplies
- Following strict protocols and safety standards
These techs ensure that every instrument used in a medical setting is clean, sterile, and functional eliminating the risk of infections and complications.
Why Is This Role So Important?
Imagine a surgeon about to perform heart surgery. What if one of the tools is contaminated or malfunctioning? That’s a nightmare scenario. The sterile processing tech helps prevent such risks by ensuring everything is properly cleaned and ready.
Their work directly impacts:
- Patient safety
- Surgical success
- Infection control
- Hospital efficiency
They’re like the pit crew of the medical world making sure everything runs smoothly and safely.
How to Become a Sterile Processing Tech
1. Education Requirements
You typically need a high school diploma or GED to start training. After that, you can attend a sterile processing technician program, which can be completed in as little as 4 to 12 months.
2. Certification Programs
While certification isn’t required in all states, it’s highly recommended and sometimes preferred by employers.
Top certifications include:
- CRCST (Certified Registered Central Service Technician) from IAHCSMM
- CBSPD (Certification Board for Sterile Processing and Distribution)
These programs teach critical skills such as microbiology, infection control, instrument identification, and sterilization methods.
3. Clinical Experience
Most programs include hands-on training in hospitals or medical centers, giving you real-world experience before entering the workforce.
What Skills Do You Need?
Sterile processing might not be for everyone. It requires a combination of precision, focus, and physical stamina.
Here are some must-have skills:
- Attention to detail – even a tiny mistake can cause infection
- Time management – hospitals run on tight schedules
- Communication – techs often coordinate with nurses and surgical staff
- Manual dexterity – handling small, delicate tools requires steady hands
- Physical endurance – you’ll be on your feet most of the day
Conclusion
Being a Sterile Processing Technician may not be glamorous, but it’s one of the most important jobs in any healthcare setting. These professionals are the silent guardians of patient safety, ensuring that every procedure starts with clean, reliable tools.
If you’re detail-oriented, organized, and passionate about healthcare, this career might be the perfect fit. With a relatively short training period and solid job prospects, it’s a great way to break into the medical field and make a real impact every single day.
FAQs
Q1: Do you need a degree to become a sterile processing tech?
No, most positions only require a certificate from a training program and a high school diploma or GED.
Q2: How long does it take to become certified?
Training programs typically last between 4 and 12 months, depending on whether you study full-time or part-time.
Q3: Is the job physically demanding?
Yes. You’ll be on your feet most of the day and handling equipment that requires attention and care.
Q4: Can you work your way up from this position?
Absolutely. Many techs become supervisors or transition into surgical technology or related fields.
Q5: Is sterile processing a good career?
Yes! It offers job security, decent pay, and the opportunity to work in the healthcare field without years of schooling.